With their more sophisticated procedures, dentists are helping people keep their teeth longer. Because people are living longer and more stressful lives, they are exposing their teeth to many more years of crack-inducing habits, such as clenching, grinding, and chewing on hard objects. These habits make our teeth more susceptible to cracks.
How do I know if my tooth is cracked?
Cracked teeth show a variety of symptoms, including erratic pain when chewing, possibly with release of biting pressure, or pain when your tooth is exposed to temperature extremes. In many cases, the pain may come and go, and your dentist may have difficulty locating which tooth is causing the discomfort.
Why does a cracked tooth hurt?
To understand why a cracked tooth hurts, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is the inner soft tissue called the pulp. The loose pulp is a connective tissue that contains cells, blood vessels and nerves.
When the outer hard tissues of the tooth are cracked, chewing can cause movement of the pieces, and the pulp can become irritated. When biting pressure is released, the crack can close quickly, resulting in a momentary, sharp pain. Irritation of the dental pulp can be repeated many times by chewing. Eventually, the pulp will become damaged to the point that it can no longer heal itself. The tooth will not only hurt when chewing but may also become sensitive to temperature extremes. In time, a cracked tooth may begin to hurt all by itself. Extensive cracks can lead to infection of the pulp tissue, which can spread to the bone and gum tissue surrounding the tooth.
How will my cracked tooth be treated?
There are many different types of cracked teeth. The treatment and outcome for your tooth depends on the type, location, and extent of the crack.
Craze Lines:
Craze lines are tiny cracks that affect only the outer enamel. These cracks are extremely common in adult teeth. Craze lines are very shallow, cause no pain, and are of no concern beyond appearances.
Fractured Cusp:
When a cusp (the pointed part of the chewing surface) becomes weakened, a fracture sometimes results. The weakened cusp may break off by itself or may have to be removed by the dentist. When this happens, the pain will usually be relieved. A fractured cusp rarely damages the pulp, so root canal treatment is seldom needed. Your tooth will usually be restored with a full crown by your dentist.
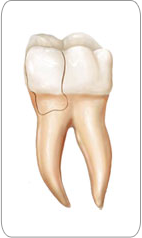
Cracked Tooth:
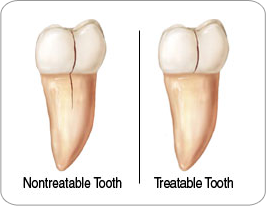
This crack extends from the chewing surface of the tooth vertically towards the root. A cracked tooth is not completely separated into two distinct segments. Because of the position of the crack, damage to the pulp is common. Root canal treatment is frequently needed to treat the injured pulp. Your dentist will then restore your tooth with a crown to hold the pieces together and protect the cracked tooth. At times, the crack may extend below the gingival tissue line, requiring extraction. A nontreatable tooth is shown in the graphic above.
Early diagnosis is important. Even with high magnification and special lighting, it is sometimes difficult to determine the extent of a crack. A cracked tooth that is not treated will progressively worsen, eventually resulting in the loss of the tooth. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in saving these teeth.
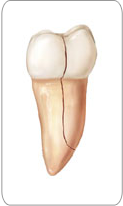
Split Tooth:
A split tooth is often the result of the long term progression of a cracked tooth. The split tooth is identified by a crack with distinct segments that can be separated. A split tooth cannot be saved intact. The position and extent of the crack, however, will determine whether any portion of the tooth can be saved. In rare instances, endodontic treatment and a crown or other restoration by your dentist may be used to save a portion of the tooth.
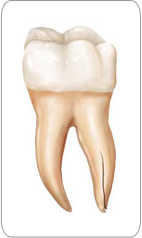
Vertical Root Fracture:
Vertical root fractures are cracks that begin in the root of the tooth and extend toward the chewing surface. They often show minimal signs and symptoms and may therefore go unnoticed for some time. Vertical root fractures are often discovered when the surrounding bone and gum become infected. Treatment may involve extraction of the tooth. However, endodontic surgery is sometimes appropriate if a portion of the tooth can be saved by removal of the fractured root.
After treatment for a cracked tooth, will my tooth completely heal?
Unlike a broken bone, the fracture in a cracked tooth will not heal. In spite of treatment, some cracks may continue to progress and separate, resulting in loss of the tooth. Placement of a crown on a cracked tooth provides maximum protection but does not guarantee success in all cases.
The treatment you receive for your cracked tooth is important because it will relieve pain and reduce the likelihood that the crack will worsen. Once treated, most cracked teeth continue to function and provide years of comfortable chewing. Talk to your endodontist about your particular diagnosis and treatment recommendations. They will advise you on how to keep your natural teeth and achieve optimum dental health.
What can I do to prevent my teeth from cracking?
While cracked teeth are not completely preventable, you can take some steps to make your teeth less susceptible to cracks.
Don't chew on hard objects such as ice, unpopped popcorn kernels or pens:
- Don't clench or grind your teeth
- If you clench or grind your teeth while you sleep, talk to your dentist about getting a retainer or other mouthguard to protect your teeth
- Wear a mouthguard or protective mask when playing contact sports